Citalopram Hydrobromide and Tinnitus: Key Facts & What to Watch For
Explore how citalopram hydrobromide may trigger or worsen tinnitus, who’s most at risk, and practical steps to manage the ringing in your ears.
Read MoreHearing loss can sneak up on you. One day you’re fine, the next you keep asking people to repeat themselves or the TV sounds too quiet. That frustration matters — hearing affects work, relationships, and safety. This page gives clear steps to spot problems, decide when to get help, and save on treatment and supplies.
There are three simple ways to think about hearing loss: conductive (sound can’t get through the ear), sensorineural (damage to the inner ear or nerve), and mixed. Watch for these signs: speech sounds muffled, trouble following conversations in noisy places, needing higher volume on devices, ringing (tinnitus), pain, or drainage from the ear. Sudden loss in one ear or dizziness with hearing loss is a red flag — don’t wait.
For kids, signs include not responding to soft sounds, delayed speech, or asking to repeat things often. In adults, difficulty on the phone or avoiding social settings is a common early sign.
Start with a hearing test. An audiologist or ENT will check hearing levels and look inside the ear. Treatments depend on cause: earwax removal can fix many cases quickly. Bacterial ear infections often need antibiotics or ear drops. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss is sometimes treated with oral steroids — early treatment improves chances. For long-term sensorineural loss, hearing aids or cochlear implants are the main solutions. Some conditions require surgery, like persistent middle ear problems.
Hearing aids come in many styles and prices. Modern devices offer Bluetooth, rechargeable batteries, and noise reduction. An audiologist can program them to match your hearing test. If you’re a candidate for a cochlear implant, an ENT will explain surgery and outcomes.
Never try to remove a deep object yourself. Cotton swabs push wax deeper and can damage the ear drum. Use safe drops recommended by a clinician or get professional microsuction or irrigation.
Prevention is simple: protect ears from loud noise, keep volume moderate on headphones, treat ear infections early, and manage chronic conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure that can affect hearing.
Want to save money? Compare prices for prescription ear drops and steroids — pharmacies in Mexico often list lower prices for the same medicines. Look for licensed pharmacies, check for generics, and keep your prescription ready. For hearing aids, shop around: clinics offer trade-ins, payment plans, and warranties. Some people buy hearing aid accessories and batteries from Mexico to cut ongoing costs, but always verify product authenticity.
If you suspect hearing loss, book a test sooner rather than later. Early action keeps more hearing and gives you options. If you need help finding affordable meds or hearing supplies, our site compares prices and points to trusted Mexican pharmacy options to help you save without risking your health.

Explore how citalopram hydrobromide may trigger or worsen tinnitus, who’s most at risk, and practical steps to manage the ringing in your ears.
Read More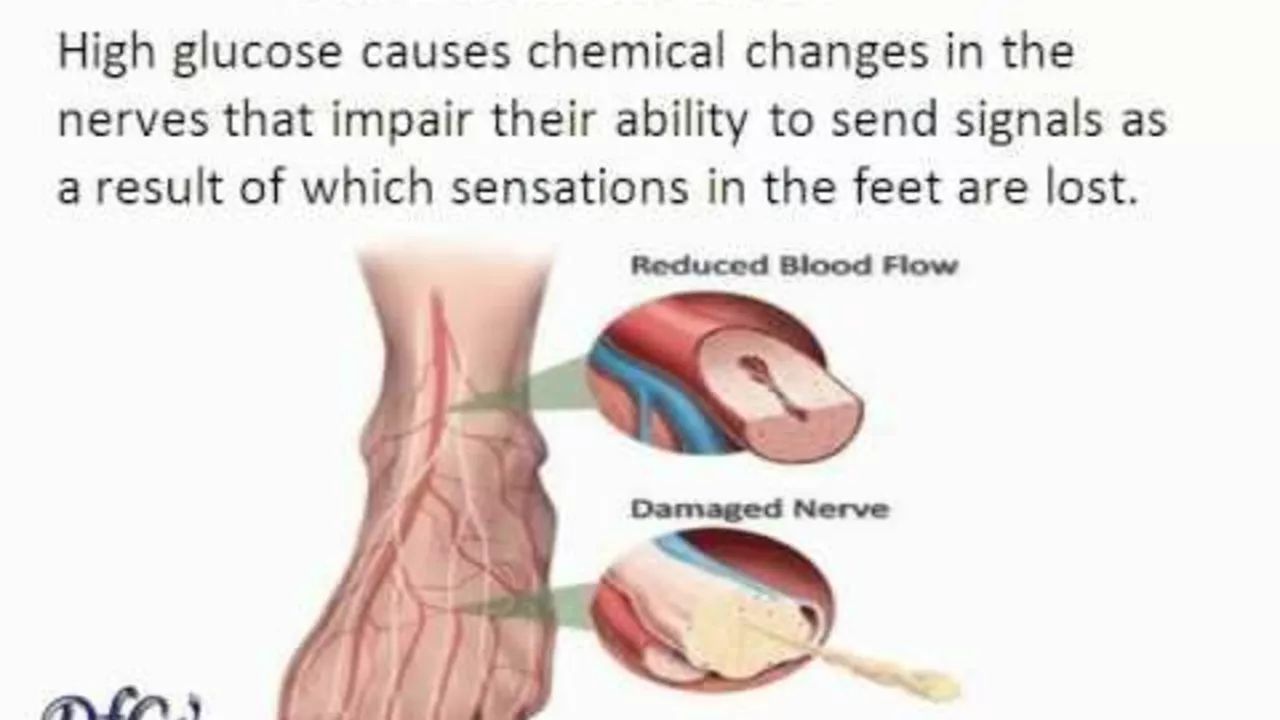
In my recent research, I've discovered a link between Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy (DPN) and hearing loss. It turns out, diabetes can damage the nerves not only in our feet and hands but also in our auditory system leading to hearing impairment. The high blood sugar levels typical in diabetes can harm the delicate nerves in our ears, leading to DPN. Thus, it's important for those with diabetes to regularly check their hearing. This connection is a crucial reminder of the far-reaching impacts of this chronic disease.
Read More